Introduction to Electric and Hybrid Cars
Electric and hybrid cars represent two significant advancements in the automotive industry aimed at promoting environmentally friendly transportation. Electric cars, as the name suggests, are vehicles that run entirely on electricity. They utilize rechargeable batteries to power an electric motor, providing a level of efficiency and zero emissions that traditional gasoline-powered vehicles cannot match. By eliminating the internal combustion engine, electric cars contribute to reducing air pollution and dependence on fossil fuels.

In contrast, hybrid cars combine both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. These vehicles can operate on either the gasoline engine, the electric motor, or both simultaneously. The design enables hybrid cars to achieve better fuel efficiency compared to conventional vehicles while still providing the flexibility of a gasoline engine when needed. This versatility is particularly beneficial for drivers who may require longer ranges that pure electric vehicles may not offer, especially in areas lacking adequate charging infrastructure.
Statistics indicate a rising trend in the adoption of both electric and hybrid cars. According to recent reports, electric vehicle sales have surged significantly, with numbers doubling in certain markets within the past few years. Hybrid cars also exhibit substantial growth, capturing a notable share of the automotive market as consumers increasingly seek more sustainable options without compromising range or performance. This growing interest can be attributed to a combination of governmental incentives, advancements in battery technology, and a broader societal shift towards eco-friendly practices.
Understanding the key features and differences between electric and hybrid cars is vital for consumers considering a car comparison. By evaluating the pros and cons of each vehicle type, individuals can make informed decisions based on their driving habits, environmental concerns, and financial considerations. This exploration leads to a deeper understanding of which vehicle may be the most suitable choice based on individual lifestyle and preferences.
Understanding Electric Cars
Electric cars represent a major advancement in automotive technology, utilizing electric motors powered by batteries rather than conventional internal combustion engines. These vehicles are often lauded for their efficiency and environmentally friendly operation. The core components of an electric vehicle (EV) include a high-capacity battery pack, which stores the electricity required for propulsion, and an electric motor, responsible for driving the wheels. The absence of a traditional engine results in a quieter, more responsive driving experience.
The performance characteristics of electric cars are particularly noteworthy. With instant torque delivery from the electric motor, these vehicles can accelerate more quickly than many gasoline-powered cars, providing a unique driving experience. Additionally, electric vehicles typically feature regenerative braking systems, which recapture energy during braking and convert it back into electricity to recharge the battery. This efficient energy management can enhance the vehicle’s overall range and performance.
As electric vehicles gain popularity, the infrastructure for charging them is increasingly being developed. Charging stations can be found at various locations, including shopping centers, parking lots, and along major highways, enabling drivers to recharge their vehicles conveniently. Home charging solutions, such as residential wall connectors and portable chargers, also play a critical role in the ownership of electric cars. Factors such as charging time, battery capacity, and range vary considerably among different models, making it essential for potential buyers to conduct a detailed comparison between electric and hybrid vehicles to understand which option suits their needs best.
Various types of electric cars are available in the market, including battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which run solely on electricity, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), combining an electric motor with a traditional gasoline engine. Each type offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to evaluate their features before making a purchasing decision.
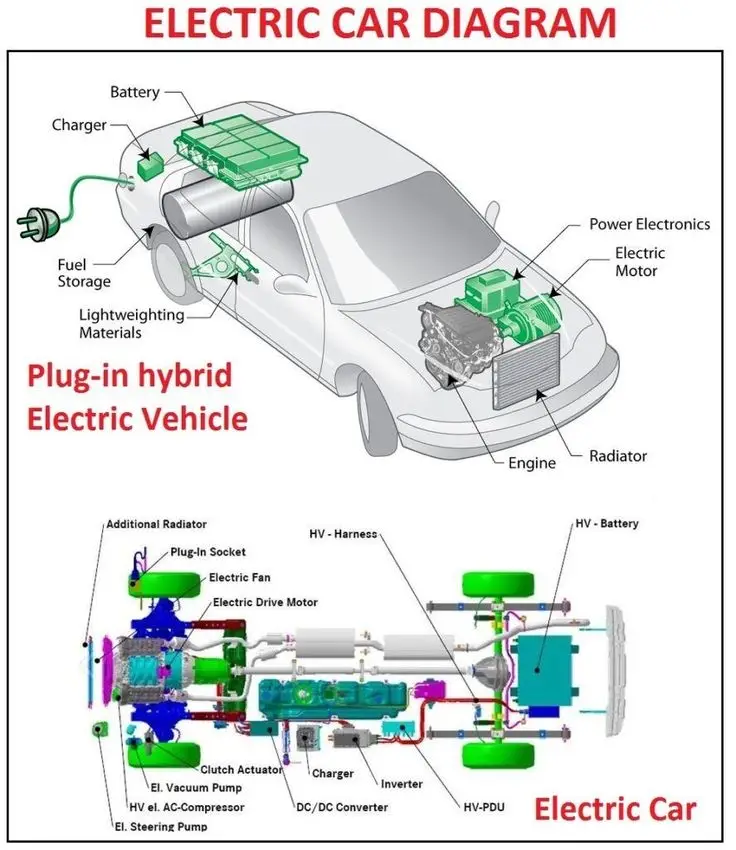
Exploring Hybrid Cars
Hybrid cars represent a noteworthy advancement in automotive technology, merging the benefits of traditional gasoline engines with electric motors. The different types of hybrid vehicles include full hybrids, plug-in hybrids, and mild hybrids, each offering distinct features and efficiencies tailored to various consumer needs.
Full hybrids can operate on either the electric motor or the internal combustion engine independently, or they can use both simultaneously. This versatility allows full hybrids to maximize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions during both city driving and highway travel. Plug-in hybrids extend this functionality further by allowing drivers to recharge their batteries via an external power source, enabling longer electric-only driving ranges before the gasoline engine kicks in. Meanwhile, mild hybrids utilize a smaller electric motor to assist the gasoline engine, enhancing fuel efficiency without the capability of operating solely on electric power.
The mechanics behind hybrid technology rely on the seamless interaction between the internal combustion engine and the electric motor. Most systems employ an energy management system that decides when to utilize the electric motor for acceleration or to recharge the battery through regenerative braking, which captures energy normally lost during braking. This combination not only improves fuel efficiency but also enhances acceleration and vehicle responsiveness.
Hybrid cars come with various advantages for consumers. They are often more fuel-efficient than their traditional counterparts, offering potential savings on fuel costs while also contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, many hybrid models qualify for tax incentives and rebates, making them financially appealing options for environmentally conscious consumers. Furthermore, the driving experience of hybrid cars tends to be quieter and smoother during electric operation, appealing to those seeking a more comfortable ride.
In conclusion, hybrid cars provide a compelling alternative for those looking to bridge the gap between traditional gasoline vehicles and fully electric cars, making them a significant consideration in any car comparison.
Environmental Impact: Electric vs Hybrid
Environmental impact is a significant consideration when choosing between electric cars and hybrid vehicles. Both options offer advantages over traditional gasoline-powered cars, but their environmental footprints differ considerably. Electric cars operate solely on electricity, which means they produce no tailpipe emissions. In contrast, hybrid cars utilize both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, leading to reduced emissions compared to conventional vehicles but still contributing to air pollution.

When evaluating emissions, it is crucial to consider the sources of electricity used to charge electric cars. In regions where renewable energy predominates, the overall emissions from electric vehicles can be dramatically reduced. Conversely, in areas reliant on fossil fuels for electricity generation, the benefits may be less pronounced. Studies show that even in the least favorable conditions, electric cars tend to have lower lifetime emissions compared to hybrid cars due to their higher energy efficiency.
Energy efficiency is another vital component in the environmental impact assessment. Electric vehicles convert over 77% of electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels, while hybrid cars convert only about 21% of the energy stored in gasoline to power. This higher efficiency results in a lower overall consumption of resources and a reduced carbon footprint for electric cars.
From a long-term sustainability perspective, the battery technology in electric vehicles is advancing rapidly, with improved recyclability and lower environmental impact than in the past. Moreover, hybrids, while more efficient than conventional cars, still rely on fossil fuels and are limited by the same drawbacks as their gasoline counterparts. Thus, a detailed comparison between electric and hybrid vehicles reveals that electric cars generally have a more favorable environmental impact overall, promoting cleaner air and a decline in greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost Considerations and Ownership Expenses
When it comes to evaluating electric cars and hybrid cars, understanding the financial implications is paramount for prospective buyers. One of the first aspects to consider is the initial purchase cost. Generally, electric cars have a higher upfront price compared to their hybrid counterparts. However, this initial cost can be mitigated through various government incentives aimed at promoting clean energy vehicles. These incentives can significantly lower the effective purchase price, making electric cars an appealing option for budget-conscious consumers.

In terms of maintenance expenses, electric cars typically fare better than hybrid cars. The absence of internal combustion engines means fewer moving parts, leading to reduced wear and lower maintenance costs. While hybrid vehicles also benefit from having a smaller engine, their complexity can result in higher maintenance expenses over time. It’s essential for buyers to factor in these differences when making a car comparison based on ownership costs.
Fuel costs represent another crucial element in the cost equation. Electric cars boast lower operating costs, particularly if drivers charge their vehicles at home during off-peak hours. Conversely, hybrid cars combine gasoline with electric power, leading to more varied fuel costs influenced by fluctuating gasoline prices. As such, a detailed comparison between electric and hybrid vehicles needs to address fuel efficiency in conjunction with how each type of vehicle performs in real-world conditions.
Additionally, projected resale values of electric cars and hybrid cars can impact long-term ownership expenses. Historically, electric cars may depreciate faster due to rapid advancements in technology, while hybrids often retain their value due to broader consumer acceptance. By weighing these financial factors, prospective car buyers can make informed decisions that align with their budgets and financial goals.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Range, and Handling
When considering a vehicle, understanding the performance metrics is crucial. In the context of our detailed comparison between electric cars and hybrid vehicles, factors such as speed, driving range, and handling play significant roles in the decision-making process.
Electric cars are often lauded for their impressive acceleration capabilities. With the absence of a traditional engine, they can deliver torque instantaneously, allowing many models to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in just a few seconds. In contrast, hybrid cars, which utilize a combination of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, typically experience slightly slower acceleration due to the added complexity of their drivetrain. However, certain high-performance hybrids can still provide robust speed that rivals standard electric vehicles.
Range is another critical aspect of performance. Electric cars tend to have varying ranges based on battery capacity, with many modern units offering between 200 to 300 miles on a single charge. The convenience of home charging and growing infrastructure of fast-charging stations are enhancing the usability of these vehicles. Conversely, hybrid cars generally boast superior range since they can operate using gasoline after the electric charge is depleted. This dual functionality allows hybrids to travel longer distances without the need for frequent charging stops.
Regarding handling, electric cars are engineered to maintain a low center of gravity thanks to their heavy battery packs, improving stability and cornering capabilities. Many drivers report a responsive and enjoyable driving experience in electric vehicles. On the other hand, hybrids may exhibit slightly less responsive handling due to their combined powertrain, though advances in technology are continuously narrowing this gap.
Ultimately, understanding these performance characteristics can help guide potential buyers in selecting between electric and hybrid vehicles based on their specific needs and preferences.
User Experience: Comfort, Technology, and Features
The user experience in electric and hybrid cars significantly varies, primarily due to their inherent technology and design. One of the most notable aspects is comfort. Electric cars often provide a quieter ride due to the absence of a traditional internal combustion engine, resulting in less engine noise and vibration. This feature is especially appreciated during longer journeys, where a serene cabin environment can enhance overall driving comfort. In comparison, hybrid vehicles, while also quieter than conventional cars, still produce some noise attributable to their gasoline engines.

Technological advancements in both electric and hybrid vehicles have rapidly evolved. Many of these cars are equipped with sophisticated infotainment systems that integrate seamlessly with smartphones, offering features such as navigation, voice commands, and connectivity options. Electric cars, in particular, are often at the forefront of these developments, incorporating cutting-edge technology such as large touchscreen displays and over-the-air software updates that enhance functionality long after the vehicle has been purchased. Hybrid cars, while featuring advanced technology, may not always match the latest innovations found in their electric counterparts.
When discussing the driving experience, features such as autonomous driving capabilities and various driver-assistance systems are increasingly common. Many electric cars include features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance as standard, which bolsters both safety and convenience. In contrast, hybrids may also offer advanced safety features, but the emphasis on pure electric mileage often leads electric models to include more innovative tech geared towards enhancing efficiency.
In conclusion, the user experiences between electric and hybrid cars differ significantly concerning comfort, technology, and features. Each type offers unique advantages, making it essential for potential buyers to evaluate their priorities and preferences when considering their next vehicle purchase.
Regulatory Framework and Incentives
The regulatory landscape for electric cars and hybrid cars is shaped by various government policies and initiatives designed to encourage the adoption of cleaner and more efficient vehicles. Many governments around the world have recognized the environmental benefits of these vehicles and have implemented measures to promote their use. This includes providing substantial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants for consumers who choose to purchase electric or hybrid vehicles over traditional gasoline-powered cars.
In the United States, for instance, federal tax incentives can amount to several thousand dollars depending on the make and model of the electric vehicle. Some states also offer additional rebates and grants that can further enhance affordability. Hybrid vehicles may also qualify for certain incentives, although often less generous than those for fully electric cars. Such financial benefits can significantly influence consumer choice, making electric cars more attractive in the marketplace.
Moreover, various regions implement specific regulations that can affect the ownership and use of these vehicles. For instance, low-emission zones in urban areas may restrict access to traditional vehicles, compelling consumers to opt for electric or hybrid alternatives. Additionally, some governments set mandates for automakers to produce a certain percentage of electric vehicles within their fleets, further shaping the availability and choice of these vehicles for consumers.
The detailed comparison between electric and hybrid vehicles, particularly in relation to regulatory incentives, illuminates how consumers are motivated to lean towards these cleaner options. By understanding the pros and cons that stem from such regulations and incentives, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their next vehicle purchase. Overall, the existing regulatory framework is a significant factor that influences consumer preferences and the market dynamics surrounding electric and hybrid cars.
Making the Choice: Which Car is Right for You?
Choosing between electric cars and hybrid vehicles can be a significant decision that depends on various personal factors. To make an informed choice, it is essential to evaluate your unique needs, preferences, and lifestyle. Here are some key considerations to help guide your decision-making process.

Firstly, consider your daily driving habits. If you frequently drive short distances within urban environments, electric cars could be an ideal option. They excel in city driving, provide instant torque, and have the advantage of zero emissions. However, for individuals who often embark on longer journeys, the versatility of hybrid cars might be more appealing. These vehicles combine an electric motor with a gasoline engine, allowing for greater range without the need for constant recharging.
Your local infrastructure also plays a critical role in your decision. Ensure there are adequate charging stations available if you choose an electric vehicle. In contrast, hybrid cars can refuel at any gas station, making them more convenient in areas devoid of extensive electric charging networks.
Another aspect to think about is your environmental values. While both electric and hybrid vehicles offer a reduction in emissions compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, electric cars represent a more sustainable option, especially when powered by renewable energy sources.
Additionally, consider the financial aspects. Electric cars may have higher upfront costs, although potential savings come from reduced fuel and maintenance expenses over time. Conversely, hybrid vehicles can sometimes offer greater initial affordability while still providing fuel efficiency.
Ultimately, a detailed comparison between electric and hybrid vehicles, considering all their pros and cons, will assist you in determining which type aligns best with your driving patterns, values, and financial situation. Engaging in thorough research and reflecting on the questions outlined can further assist in making the right choice for your circumstances.